厦门大学电子科学与技术学院(国家示范性微电子学院), 福建 厦门 361005
以被动锁模正色散掺镱(Yb)光纤激光器为研究对象,实验比较研究了激光腔内滤波带宽对产生正色散束缚态孤子的影响。采用高掺Yb光纤作为增益介质,半导体饱和吸收镜作为锁模部件,获得1064 nm全光纤线型腔锁模激光器。当腔内带通滤波器选用不同带宽(0.2,1.0,1.2,2.3 nm)时,观察到不同的皮秒锁模脉冲状态。在滤波带宽较小(0.2 nm)或较大(2.3 nm)时,仅产生稳定的单脉冲耗散孤子;相反地,在滤波带宽适中(1.0 nm或1.2 nm)时,分别观察到典型的相位差为π和-π/2束缚态耗散孤子,脉宽和脉冲间隔均分别为3 ps和14 ps。将束缚态耗散孤子激光通过主控振荡功率放大技术放大至1.4 W后,将其注入到光子晶体光纤中,获得了750~1600 nm超连续谱(10 dB谱宽),输出功率约为0.7 W,相比传统耗散孤子抽运具有更好的光谱平坦性。
激光器 束缚态孤子 滤波带宽 超连续谱

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
Raman and Brillouin lasers based on a high-quality (high-Q) whispering gallery mode microresonator (WGMR) are usually achieved by employing a tunable single-frequency laser as a pump source. Here, we experimentally demonstrate visible Raman and Brillouin lasers using a compact microresonator/ZrF4 BaF2 LaF3 AlF3 NaF (ZBLAN)-fiber hybrid system by incorporating a WGMR with a fiber-compatible distributed Bragg reflector/fiber Bragg grating to form a Fabry–Perot (F-P) fiber cavity and using a piece of Pr:ZBLAN fiber as gain medium. The high-Q silica-microsphere not only offers a Rayleigh-scattering-induced backreflection to form the ~635 nm red laser oscillation in the F-P fiber cavity, but also provides a nonlinear gain in the WGMR itself to generate either stimulated Raman scattering or stimulated Brillouin scattering. Up to six-order cascaded Raman lasers at 0.65 μm, 0.67 μm, 0.69 μm, 0.71 μm, 0.73 μm, and 0.76 μm are achieved, respectively. Moreover, a Brillouin laser at 635.54 nm is clearly observed. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first demonstration of visible microresonator-based lasers created by combining a Pr:ZBLAN fiber. This structure can effectively extend the laser wavelength in the WGMR to the visible waveband and may find potential applications in underwater communication, biomedical diagnosis, microwave generation, and spectroscopy.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(5): 05000566

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Information and Communication Branch, State Grid Jiangxi Electric Power Corporation Ltd., Nanchang 330077, China
2 Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
We demonstrate a 2080 nm long-wavelength mode-locked thulium (Tm)-doped fiber laser operating in the dissipative soliton resonance (DSR) regime. The compact all-fiber dumbbell-shaped laser is simply constructed by a 50/50 fiber loop mirror (FLM), a 10/90 FLM, and a piece of large-gain Tm-doped double-clad fiber pumped by a 793 nm laser diode. The 10/90 FLM is not only used as an output mirror, but also acts as a periodical saturable absorber for initiating DSR mode locking. The stable DSR pulses are generated at the center wavelength as long as 2080.4 nm, and the pulse duration can be tunable from 780 to 3240 ps as the pump power is increased. The maximum average output power is 1.27 W, corresponding to a pulse energy of 290 nJ and a nearly constant peak power of 93 W. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the longest wavelength for DSR operation in a mode-locked fiber laser.
060.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.4050 Mode-locked lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(3): 030602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
Conventional Q-switched fiber lasers operating at multi-longitudinal-mode oscillation usually suffer from self-mode-locking-induced temporal instability, relatively strong noise, and low coherence. Here, we address the challenge through demonstrating, for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, a single-longitudinal-mode (SLM) Er-doped fiber (EDF) laser passively Q-switched by a few-layer Bi2Se3 saturable absorber (SA). The Bi2Se3 SA prepared by the liquid-phase exfoliation method shows a modulation depth of ~5% and saturation optical intensity of 1.8 MW/cm2. A section of 1-m unpumped EDF together with a 0.06-nm-bandwidth fiber Bragg grating is used as an ultra-narrow autotracking filter to realize SLM oscillation. Stable SLM Q-switching operation at 1.55 μm is successfully achieved with the spectral linewidth as narrow as 212 kHz and the pulse duration of 2.54 μs, manifesting near-transform-limited pulses with a time-bandwidth product of 0.53. In particular, we found that the SLM Q-switching possesses the higher signal-to-noise ratios of 62 dB (optical) and 48 dB (radio frequency), exhibiting its advantages of low noise and high stability. Such an SLM Q-switched fiber laser could gain great interest for some applications in coherent detection, coherent optical communications, and high-sensitivity optical sensing.
Lasers, fiber Lasers, Q-switched Photonics Research
2018, 6(10): 10000C29
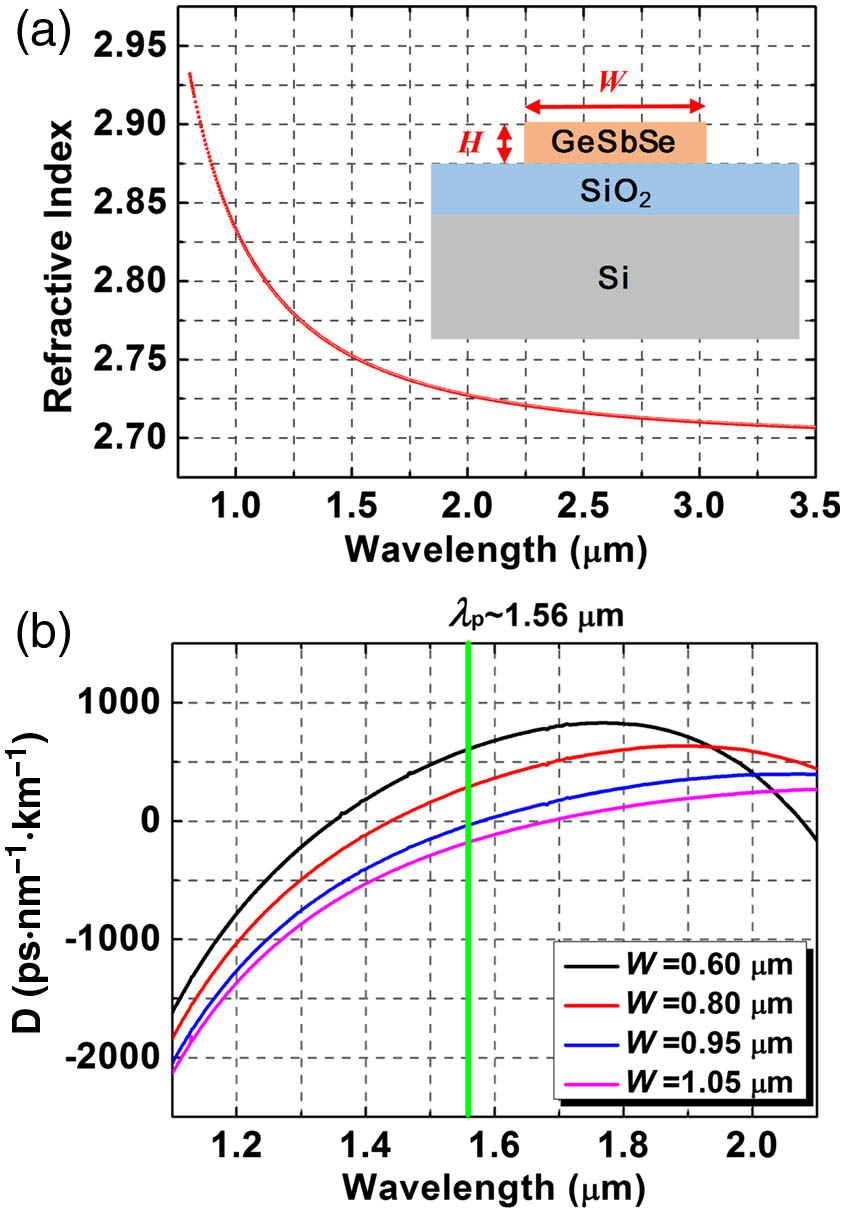
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139, USA
2 Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
3 College of Information Science and Electronic Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
4 Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Materials and Devices of Zhejiang Province, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
On-chip spectroscopic sensors have attracted increasing attention for portable and field-deployable chemical detection applications. So far, these sensors largely rely on benchtop tunable lasers for spectroscopic interrogation. Large footprint and mechanical fragility of the sources, however, preclude compact sensing system integration. In this paper, we address the challenge through demonstrating, for the first time to our knowledge, a supercontinuum source integrated on-chip spectroscopic sensor, where we leverage nonlinear Ge22Sb18Se60 chalcogenide glass waveguides as a unified platform for both broadband supercontinuum generation and chemical detection. A home-built, palm-sized femtosecond laser centering at 1560 nm wavelength was used as the pumping source. Sensing capability of the system was validated through quantifying the optical absorption of chloroform solutions at 1695 nm. This work represents an important step towards realizing a miniaturized spectroscopic sensing system based on photonic chips.
Sensors Supercontinuum generation Photonics Research
2018, 6(6): 06000506
研究了一种适用于无导光板侧入掠射式发光二极管(LED)平板灯的双面三棱柱阵列微结构扩散板。通过菲涅耳公式理论分析了双面三棱柱阵列增透原理,利用光线追迹软件TracePro模拟仿真了三棱柱阵列深宽比和三棱柱底边宽度对扩散板透射率的影响。模拟结果表明,入射面的透射率随深宽比的增大而增大,对于聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA)和聚碳酸酯(PC)光学材料,当深宽比为0.5左右时透射率达到最大,并不再随深宽比增大而改变。出射面三棱柱阵列微结构深宽比在0.5附近由于两次全内反射导致透射率出现一个下降区域,而三棱柱阵列间距对扩散板的透射率影响很小,结果表明优化后的三棱柱微结构阵列扩散板对掠射光线的透射率可达93%。
光学设计 扩散板 菲涅耳公式 三棱柱微结构
华侨大学 信息科学与工程学院, 福建省光传输与变换重点实验室, 福建 厦门 361021
使用连续式输出的砷化镓半导体激光器泵浦的掺钕钒酸钇激光器作为光源,利用磷酸氧钛钾晶体腔内倍频产生波长为532 nm的绿光,通过轴棱锥产生了近似无衍射贝塞尔光束。推导了倍频产生的绿光的场分布,并模拟了倍频绿光经过轴棱锥产生的近似无衍射光束的轴向光强分布图和截面光强分布图。通过实验拍摄了距离轴棱锥不同位置的截面光强分布,测量了无衍射贝塞尔绿光的最大无衍射距离和中心光斑直径,实验数据与理论模拟基本吻合。实验结果说明所述方法产生的倍频无衍射绿光具有良好的光束质量,具有应用价值。
半导体激光器 贝塞尔光束 倍频 轴棱锥 laser diode Bessel beam frequency doubling axicon 强激光与粒子束
2014, 26(1): 011007
华侨大学信息科学与工程学院福建省光传输与变换重点实验室, 福建 厦门 361021
利用衍射积分理论和干涉理论分析了轴棱锥对无衍射贝塞尔(Bessel)光束进行线聚焦产生局域空心光束遇障碍发生自重建的全过程。数值模拟了周期局域空心光束的传输情况及轴上放入圆形障碍物后不同位置的截面光强分布图,并计算了障碍物后最小自重建距离。研究结果表明周期局域空心光束遇到障碍物后,会绕过障碍物继续向前传输,并且传输一段距离后恢复原来的周期局域空心光束的特性。设计实验光路图对理论模拟进行了验证,通过显微镜和照相机系统拍摄得到轴上圆形障碍物和方形障碍物前后光束的截面光强分布图,实验与理论模拟相吻合。研究结果使得周期局域空心光束的应用得到了扩展。
衍射 周期局域空心光束 障碍物 自重建
华侨大学信息科学与工程学院福建省光传输与变换重点实验室, 福建 厦门 361021
利用干涉理论对无衍射贝塞尔光束经轴棱锥线聚焦后产生的周期局域空心光束进行描述。计算了产生的局域空心光束的最大无衍射距离。采用几何光学理论和干涉理论对轴棱锥聚焦无衍射光束进行分析,并利用MathCAD软件对沿传输距离变化的光强分布和一个周期内光强的演变情况及对应的光斑图进行数值模拟。实验中采用一个底角为1°的轴棱锥来产生无衍射贝塞尔光束,再经第二个底角为2°的轴棱锥对无衍射贝塞尔光束进行聚焦,通过显微镜和CCD照相机系统对光束进行观察和拍摄,实验和模拟结果相吻合。
几何光学 干涉理论 线聚焦 贝塞尔光束 周期局域空心光束 光强分布
华侨大学 信息科学与工程学院, 福建 泉州 362021
分析了三种不同频谱宽度的光源(激光、绿光LED和白光LED)产生无衍射贝塞尔(Bessel)光束亮暗环的梯度。分别模拟得到在不同位置的光强截面图, 并计算各亮暗环的光强值, 引入对比度的计算公式, 计算了三种不同频谱宽度的光源产生贝塞尔光束亮暗环的对比度, 可以得到频谱宽度越宽的光源产生的贝塞尔光束亮暗环之间的对比度降低, 亮暗环强度梯度下降, 从而导致囚禁粒子的能力降低。根据三种光源的特性设计了实验装置, 并在与理论模拟相应的位置分别拍摄了三种不同频谱宽度光源产生的无衍射光斑图。对实验中拍摄到的光斑图进行对比度计算, 可以得知频谱宽度越宽的光源产生的无衍射光束, 其截面光斑亮暗环的对比度降低, 亮暗环强度梯度降低, 囚禁粒子能力下降, 理论和实验相吻合。
Bessel光束 频谱宽度 对比度 粒子囚禁 强度梯度 Bessel beam spectral width contrast particle confinement intensity gradient





